문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/9370
코드
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 987654321;
int tc, n, m, t, s, g, h, a, b, c, x1, distS[2003], distG[2003], distH[2003];
vector<pair<int, int>> adj[2003];
vector<int> destination;
void init()
{
for(int i = 0; i < 2003; i++)
{
adj[i].clear();
}
fill(distS, distS+2003, INF);
fill(distG, distG+2003, INF);
fill(distH, distH+2003, INF);
destination.clear();
}
void input()
{
//교차로 = vertex, 도로 = edge , 목적지 후보의 개수
cin >> n >> m >> t;
//출발지, g, h
cin >> s >> g >> h;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
cin >> a >> b >> c;
adj[a].push_back({c, b});
adj[b].push_back({c, a});
}
for(int i = 0; i < t; i++)
{
//목적지 후보
cin >> x1;
destination.push_back(x1);
}
}
void dijkstra(int start, int *dist)
{
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> pq;
pq.push({0, start});
dist[start] = 0;
while(pq.size())
{
int curDist = pq.top().first;
int curVertex = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < adj[curVertex].size(); i++)
{
int nextDist = adj[curVertex][i].first;
int nextVertex = adj[curVertex][i].second;
if(dist[nextVertex] > curDist + nextDist)
{
dist[nextVertex] = curDist + nextDist;
pq.push({dist[nextVertex], nextVertex});
}
}
}
}
void findDestination()
{
sort(destination.begin(), destination.end());
for(int i = 0; i < destination.size(); i++)
{
int dest = destination[i];
//G->H 방향으로 지나는 경우
if(distS[dest] == distS[g] + distG[h] + distH[dest])
cout << dest << " ";
//H->G 방향으로 지나는 경우
else if(distS[dest] == distS[h] + distH[g] + distG[dest])
cout << dest << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
cin >> tc;
while(tc--)
{
init();
input();
dijkstra(s, distS);
dijkstra(g, distG);
dijkstra(h, distH);
findDestination();
}
return 0;
}
시작지점이 정해져있고, 꼭 지나가야하는 거리가 있으며, 목적지 후보들 중에서 최단거리로 갈 수 있는 목적지 출력을 요구하는 문제이다.
최단거리 알고리즘인 다익스트라를 이용하면 된다.
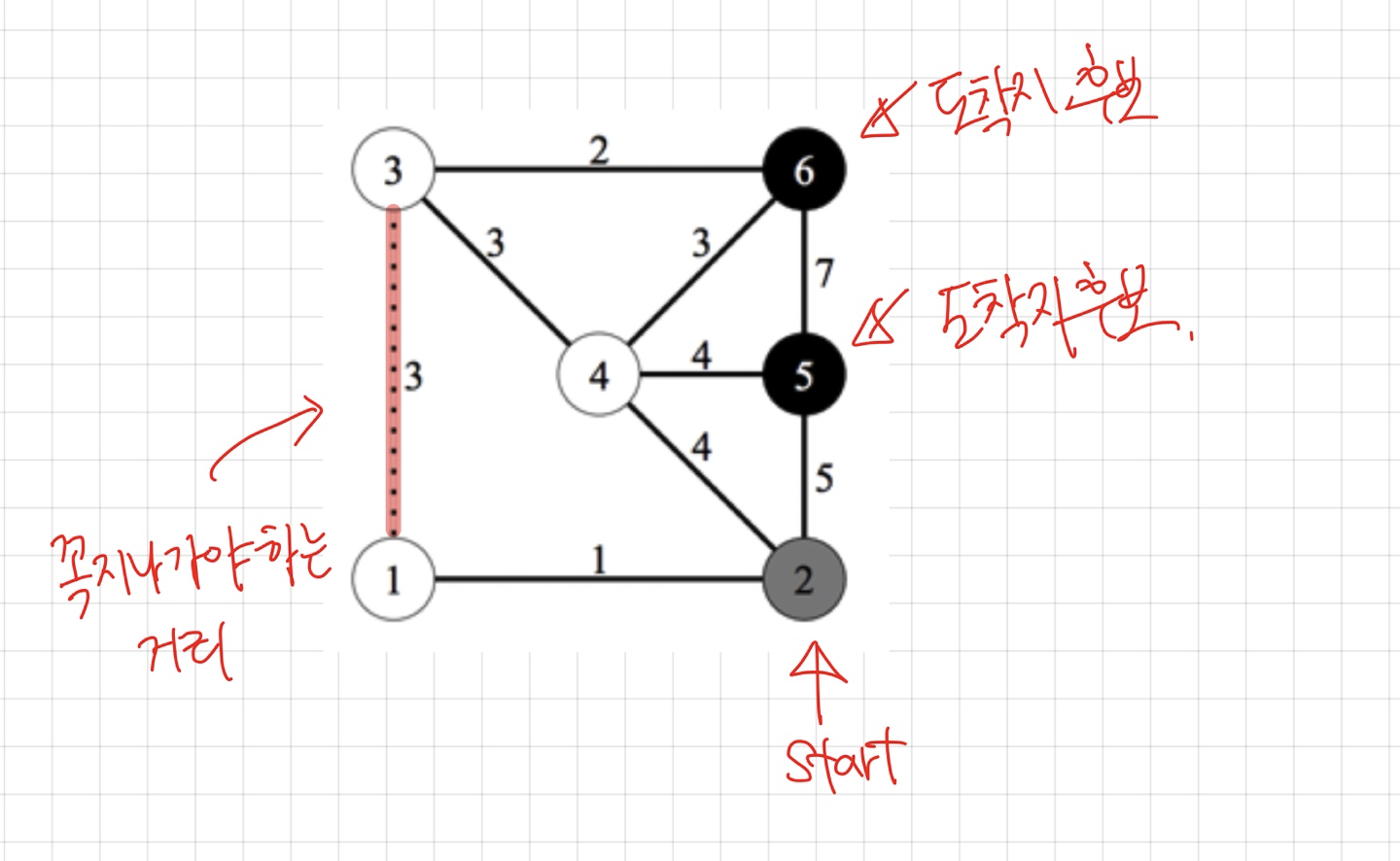
해당 문제는 양방향으로 지날갈 수 있기때문에 다음과 같은 경우의 수가 생긴다.
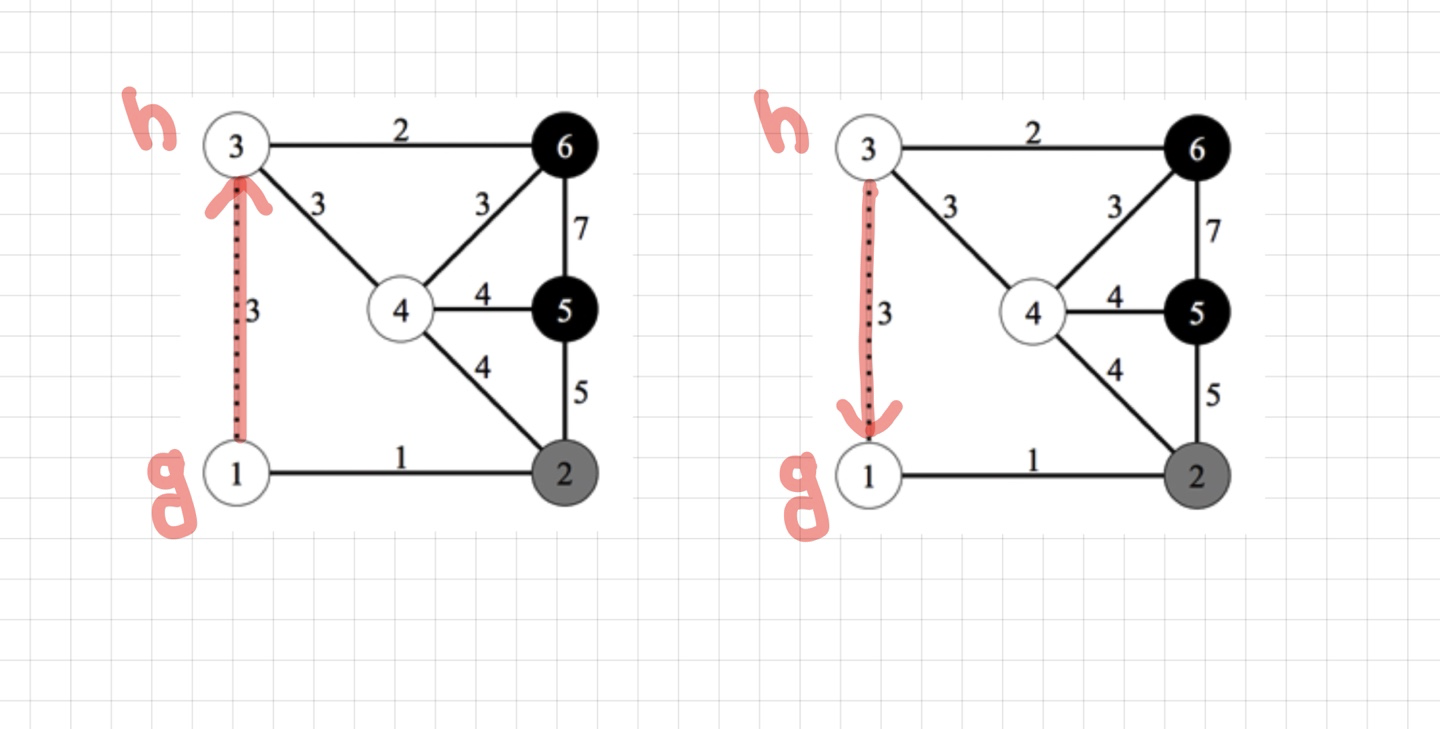
시작점에서 시작해서 g->h 로 지나가는 경우와, 시작점에서 시작해서 h->g로 지나가는 경우이다.
g->h 로 지나가는 경우는 다음과 같은 경로로 최단거리를 구할 수 있다.
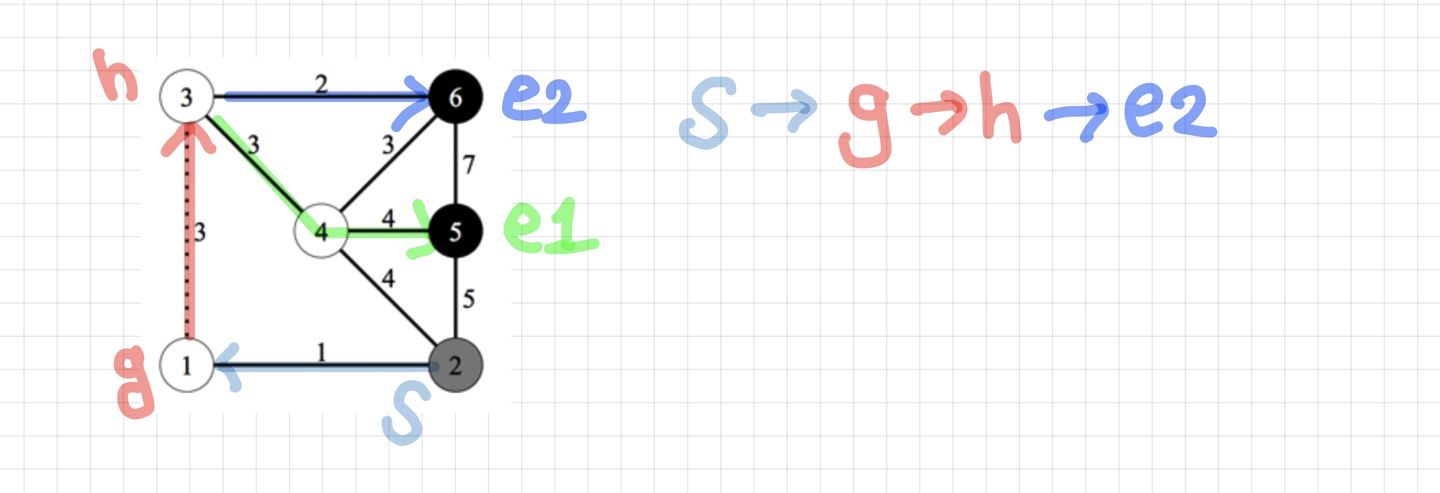
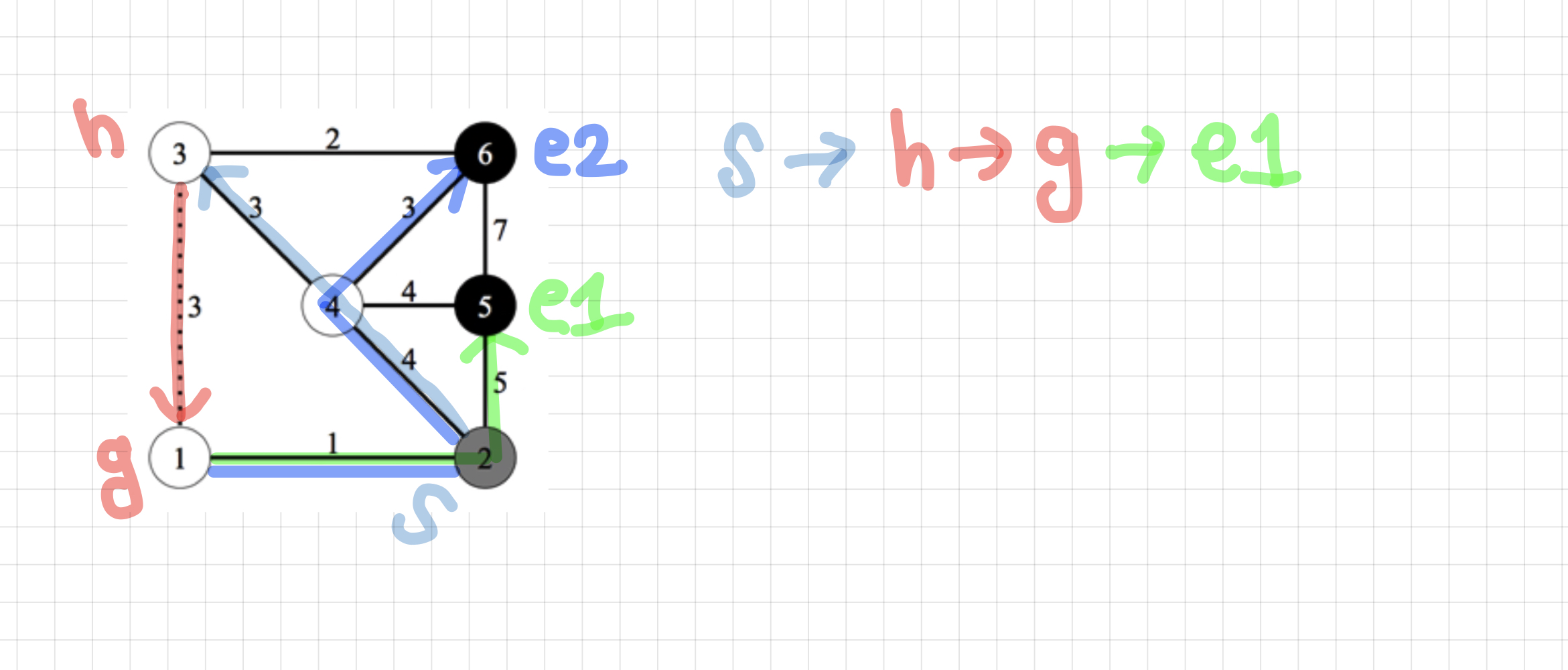
h->g로 지나가는 경우는 다음과 같은 경로로 최단거리를 구할 수 있다.
s 에서 시작하는 다익스트라 배열 하나와
g 에서 시작하는 다익스트라 배열 하나와
h 에서 시작하는 다익스트라 배열 하나를 구한 뒤
아래와 같이 목적지를 출력해주면 된다.
void findDestination()
{
sort(destination.begin(), destination.end());
for(int i = 0; i < destination.size(); i++)
{
int dest = destination[i];
//G->H 방향으로 지나는 경우
if(distS[dest] == distS[g] + distG[h] + distH[dest])
cout << dest << " ";
//H->G 방향으로 지나는 경우
else if(distS[dest] == distS[h] + distH[g] + distG[dest])
cout << dest << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
'개발 > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 1149 RGB거리 C++ (0) | 2021.06.03 |
|---|---|
| 백준 16118 달빛여우 C++ (0) | 2021.05.31 |
| 펜윅 트리란?(Fenwick Tree, Binary Indexed Tree) (0) | 2021.05.28 |
| 누적합(Prefix Sum) 이란? (0) | 2021.05.27 |
| 백준 5719 거의최단경로 C++ (0) | 2021.05.27 |


